-
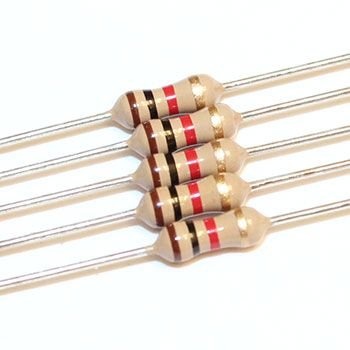
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistors resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistors resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistors resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistors resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistors resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistors resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistors resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistors resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistors resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistors resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistors resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistors resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistors resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistors resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistors resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistors resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistors resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistors resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistors resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components that have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Common resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistors resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistors resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistors resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistors resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistors resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistors resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and cant generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components that have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Common resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull up I/O lines.
-
Resistors are electronic components which have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor’s resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can’t generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where they complement active components like op-amps, microcontrollers, and other integrated circuits. Commonly resistors are used to limit current, divide voltages, and pull-up I/O lines.
-
- 5% through hole Resistor
- 1/4 Watt
- 0.25 Watt
-
- Type: 5mm Diffuse Led
- Colors: Red, Green, Yellow, Blue and Ultra-bright White
- Pot diameter: 5mm
- Shell Material: Epoxy
- Typical working voltage: 1.9 to 2 volts
- Typical current: 20mA
- Wavelength: 620 to 625nm
- Luminous intensity: 600 to 800mcd
- The angle of view: 45
- Number of pins: 2
-
3mm Frosted LEDs bright 3mm LEDs are incredibly bright with a wide beam angle. They’re suitable for use in your projects, illuminations, car lighting, models or anywhere where you need low power, high-intensity reliable lighting or indication. They fit easily into a breadboard and will add that extra zing to your project.
The lens has a frosted effect, which distributes the light evenly. Excellent for use in all types of indicators where an unfocused light is desirable. They work well mounted in our 3mm LED Holders and the light produced from the Red, Green, Blue, Yellow, or White LED appears very crisp and clean.
-
A ceramic capacitor is a fixed-value capacitor where the ceramic material acts as the dielectric. The value of 224 ceramic capacitor is 220nF.
-
- Ceramic Type Capacitor
- 470pf (471)
- Volt; 50V
- Capacitor Tolerance: 10%.
- Color: As pictures
- Structure: Fixed capacitors
-
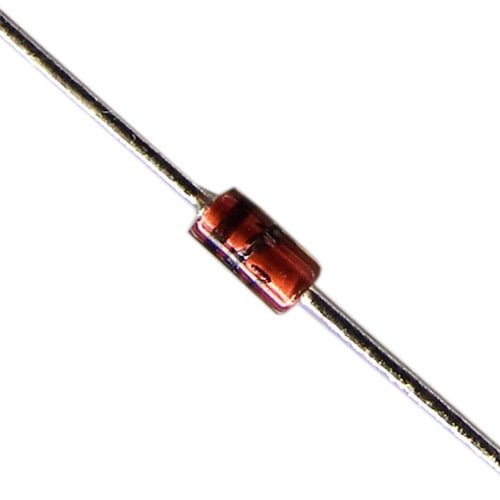
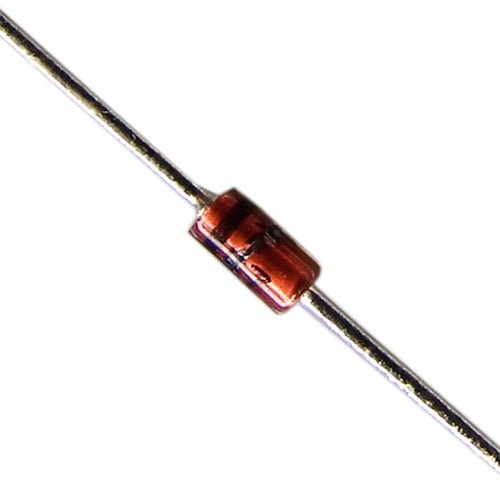
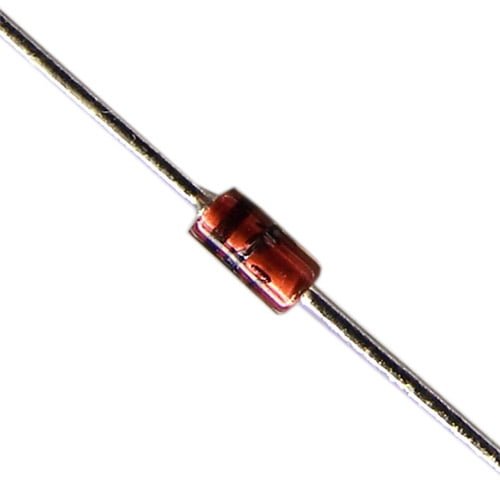
1N4007 1000V 1A General Purpose Rectifier Diode 4007
Original price was: ₨8.00.₨5.00Current price is: ₨5.00. Quick View- Maximum Recurrent Peak Reverse Voltage 1000V
- Maximum Average Forward Output Current 1A
- Maximum Forward Voltage Drop per element at 1.0A DC 1.1V
- Typical Junction Capacitance 15pF
- Package DO-41
- Weight 0.33grams
- Operating and Storage Temperature Range (65 to +175C)
-
- Average forward current is 1A
- Non-repetitive Peak current is 30A
- Reverse current is 5uA.
- RMS reverse voltage is 70V
- Peak repetitive Reverse voltage is 100V
- Available in DO-41 Package
-
IN4001 Diode 4001 Rectifier Diode
Original price was: ₨8.00.₨5.00Current price is: ₨5.00. Quick View- Package Type: Available in DO-41 & SMD Packages
- Diode Type: Silicon Rectifier General Usage Diode
- Max Repetitive Reverse Voltage is: 50 Volts
- Average Fwd Current: 1000mA
- Non-repetitive Max Fwd Current: 30A
- Max Power Dissipation is: 3W
- Max Storage & Operating temperature Should Be: -55 to +175 Centigrade
-
3.3 Volt Zener Diode, 500mW, 5% tolerance. Low noise high stability, suitable for voltage regulation or voltage dropping in low current circuitry.
DO-35 package, For more information please see BZX55 Data Sheet
-
0.5W ZENER DIODE 18V 1/2W ZENER DIODE 18V
Original price was: ₨12.00.₨8.00Current price is: ₨8.00. Quick View- Diode type: Zener Diode
- Voltage rating: 18V
- Power: 500mW
- Material type: Semiconductor
-
- Package Type: TO-92
- Transistor Type: PNP
- Max Collector Current(IC): -100mA
- Max Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCE): -45V
- Max Collector-Base Voltage (VCB): -50V
- Max Emitter-Base Voltage (VBE): -5V
- Max Collector Dissipation (Pc): 500 Milliwatt
- Max Transition Frequency (fT): 100 MHz
- Minimum & Maximum DC Current Gain (hFE): 125 to 800
- Max Storage & Operating temperature Should be: -65 to +150Centigrade
-
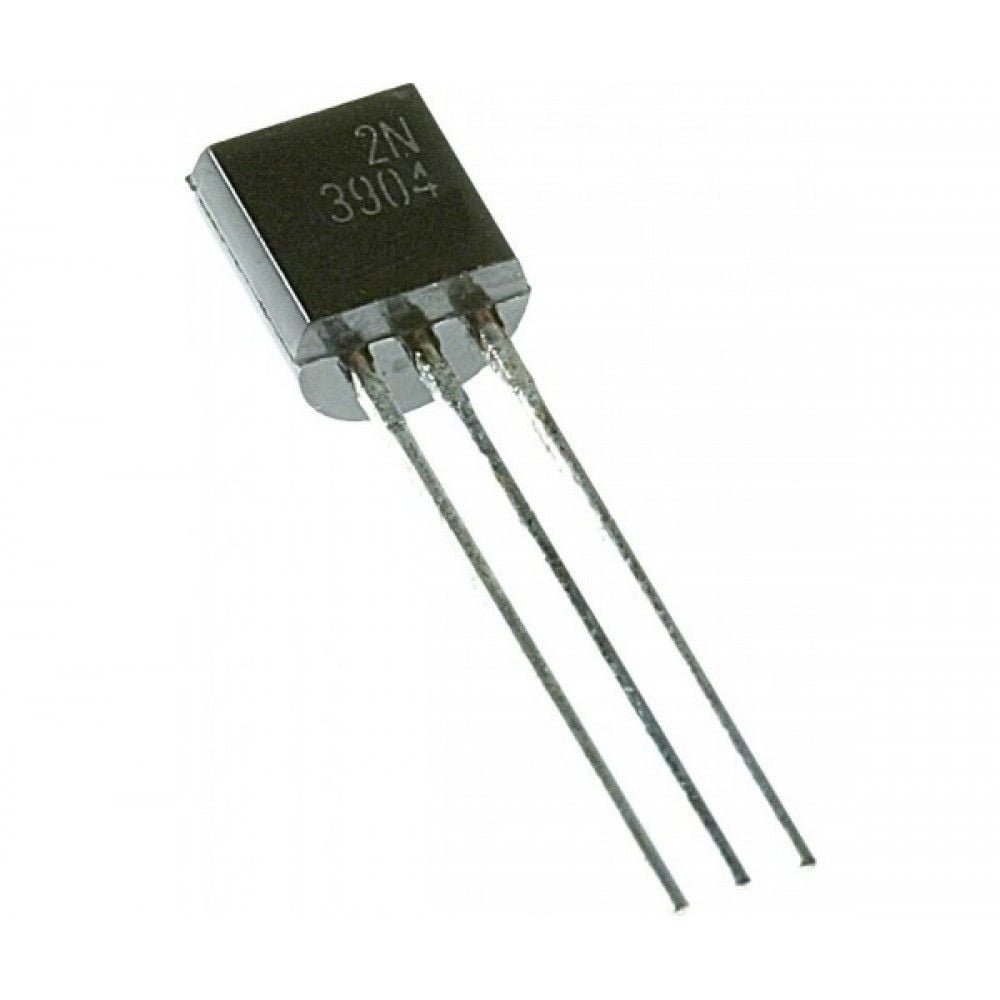
- Bi-Polar NPN Transistor
- DC Current Gain (hFE) is 800 maximum
- Continuous Collector current (IC) is 500mA
- Emitter Base Voltage (VBE) is 5V
- Base Current(IB) is 5mA maximum
- Available in To-92 Package
-
IC sockets are generally for preventing damage to IC’s from soldering and while testing multiple circuits. These are made from Black Thermoplastic and tin-plated alloy contacts. One end is notched to aid in identification. They can be mounted end to end to suit longer IC’s.
-
Specifications:
- Power (Watts) 1W
- Resistant 1K OHMS
- Tolerance +- 5%
- Resistor Type Carbon Film
- Lead Free
-
IN5819 Diode SCHOTTKY DIODE 1N5819
Original price was: ₨15.00.₨9.00Current price is: ₨9.00. Quick View- Schottky Rectifier Diode
- Average forward current is 1A
- Forward Surge Current is 25A
- Forward Voltage Drop 600mV at 1A
- Peak reverse voltage is 40V
- RMS Reverse Voltage is 28V
- Available in DO-41 Package
-
Specification of BZX55C12V0 12V 1/2W Zener Diode DO-35
Supply Voltage: BZX55C12V0 12V
Type: Low Power Switching Zener Diode
Package: DO-35
Diode Configuration: Single
Zener Voltage Tolerance: 5%
Package Type: Through Hole
Dissipation Power: 1/2 W
Dimensions: 4.25 x 1.85 x 1.85mm
Operating Temperature: -40°C to 85°C -
- Supply Voltage: 1N5340 6V
- Type: Low Power Switching Zener Diode
- Package: DO-15
- Diode Configuration: Single
- Zener Voltage Tolerance: 5%
- Package Type: Through Hole
- Dissipation Power: 5W
- Dimensions: 10.7 x 7 x .1cm
- Operating Temperature: -65°C to 200°C
-
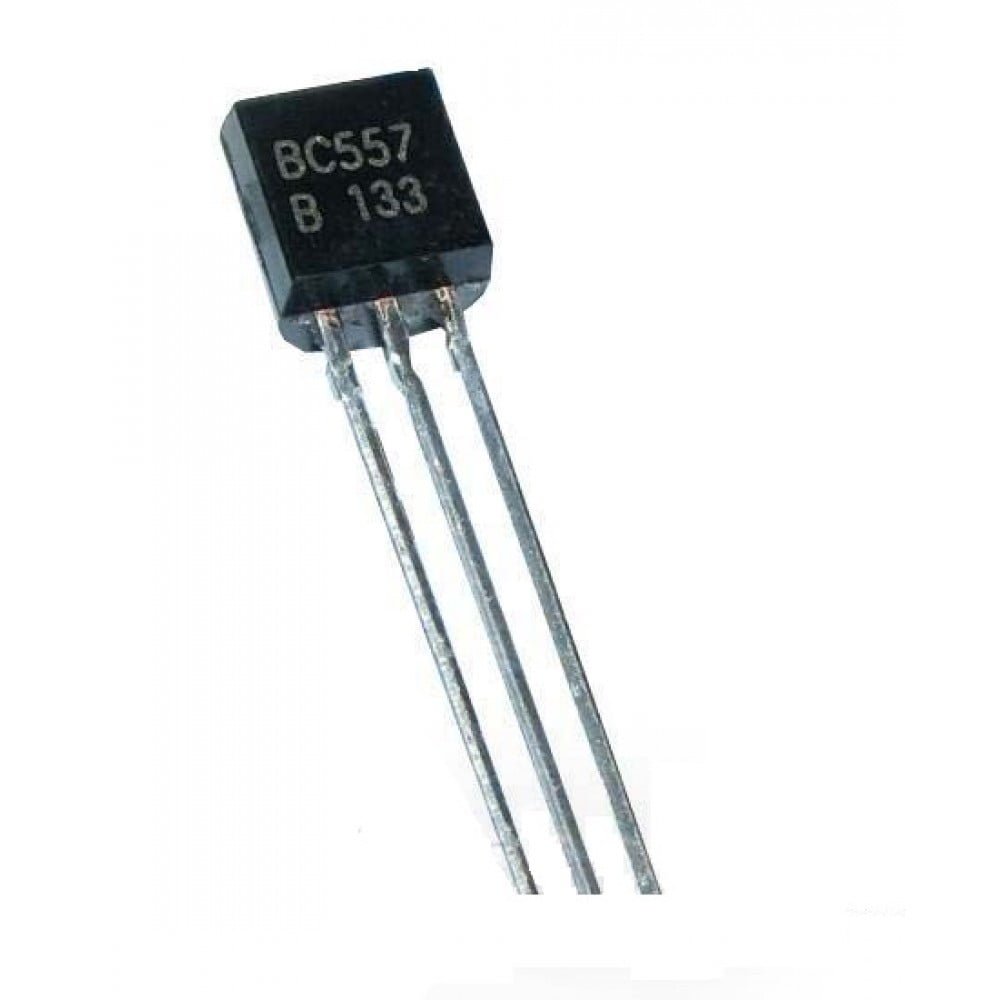
BC547-B166 NPN Transistor 50V/ 0.3A
Original price was: ₨15.00.₨9.00Current price is: ₨9.00. Quick ViewOverall, the BC547 NPN transistor is a versatile and reliable transistor that is suitable for a wide range of applications. NPN Transistor BC547 is a popular choice for electronic hobbyists and engineers because it is inexpensive and easy to use. here are the specifications of the BC547-B166 NPN transistor:
- Collector current (maximum): 300mA
- Collector-emitter voltage (maximum): 65V
- Base current (maximum): 5mA
- Current gain (hFE): 110 to 800
- Package: TO-92
-
24V 1/2W Zener Diode Zener diode 24 V 0.5W
Original price was: ₨15.00.₨10.00Current price is: ₨10.00. Quick View24V 1/2W Zener Diode product and all other general purpose diode types such as Schottky (Baritt), Zener, Crystal, Photo Diode, LED (Light Emitting Diode), Metal Case Power Diodes, Transit; You can purchase various sheath types of Silicon or Germanium models
-
5.1V Zener diode 0.5W Zener diode 5.1 V 1/2W
Original price was: ₨15.00.₨10.00Current price is: ₨10.00. Quick View5.1V Zener diode 0.5W Zener diode 5.1 V 1/2W are useful for creating a reference voltage or as a voltage stabilizer for low-current applications. These diodes are rated for 5.1 volts with a maximum of 1W. 24V 0.5W 5% Semiconductor.
-
HER107 HER-107 high efficiency rectifier diode
Original price was: ₨15.00.₨10.00Current price is: ₨10.00. Quick ViewFEATURES
Low forward voltage drop
High current capability High reliability
High surge current capability
High speed switching -
1N5408 5408 3Amp General Purpose Rectifier Diode
Original price was: ₨15.00.₨10.00Current price is: ₨10.00. Quick View1N5408 is a member of the 1N5400 series, which is a family of popular 3 A general-purpose silicon rectifier diodes. The blocking voltage of the series varies according to diode number, 1N5408 denotes 1000 volts. It is commonly used in AC Adapters, which is used in common household appliances. A general-purpose diode is a two-terminal semiconductor device. It allows current to pass only in one direction, from its anode to cathode.
-
IN4148 Diode 1N4148 / 1N914 Signal Diode
Original price was: ₨15.00.₨10.00Current price is: ₨10.00. Quick ViewVoltage – DC Reverse (Vr) (Max): 75VCurrent – Average Rectified (Io): 150mAVoltage – Forward (Vf) (Max) @ If: 1V @ 10mASpeed: Small Signal =< 200mA (Io), Any SpeedReverse Recovery Time (trr): 4nsCurrent – Reverse Leakage @ Vr: 5A @ 75VCapacitance @ Vr, F: 4pF @ 0V, 1MHzThermal Resistance: 300C/W JaMounting Type: Through HolePackage / Case: DO-204AH, DO-35, AxialSupplier Device Package: DO-35Operating Temperature – Junction: -65C ~ 175COther Names: 1N4148CT,1N4148CT-ND, 1N4148DICT, 1N914 -
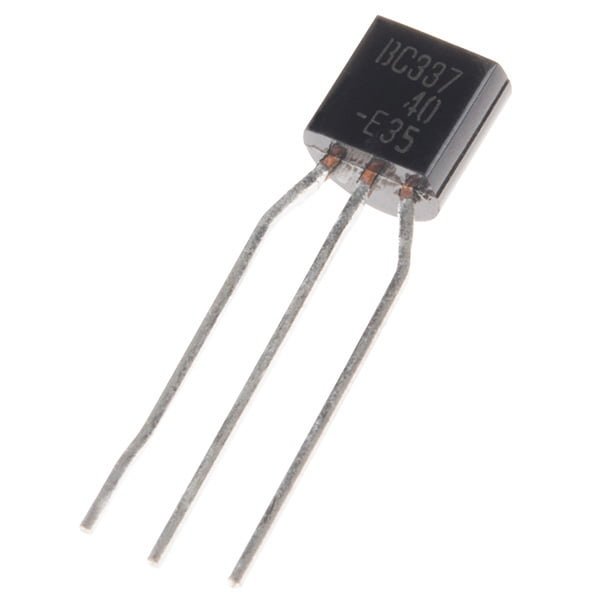
This is the BC337, an NPN silicon BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor). This little transistor can help in your project by being used to help drive large loads or amplifying or switching applications. The BC337 is specifically rated at 50V and 800mA max.
-
1K Potentiometer (Pot) is a manually adjustable variable resistor with 3 terminals. Two terminals are connected to both ends of a resistive element, and the third terminal connects to a sliding contact, called a wiper, moving over the resistive element.The position of the wiper determines the output voltage of the potentiometer. small screw driver can be used for calibration of resistance value.
-
- Resistance: 2K Ohm,
- Resistor Tolerance: ±10% Max
- Max Voltage: 50V
- Rating Power: 0.1W
- Technology: Carbon Film
- Adjustment Type: Top Adjustment
-
A potentiometer is a manually adjustable variable resistor with 3 terminals. Two terminals are connected to both ends of a resistive element, and the third terminal connects to a sliding contact, called a wiper, moving over the resistive element.The position of the wiper determines the output voltage of the potentiometer. small screw driver can be used for calibration of resistance value.
-
A potentiometer is a manually adjustable variable resistor with 3 terminals. Two terminals are connected to both ends of a resistive element, and the third terminal connects to a sliding contact, called a wiper, moving over the resistive element.The position of the wiper determines the output voltage of the potentiometer. small screw driver can be used for calibration of resistance value.
-
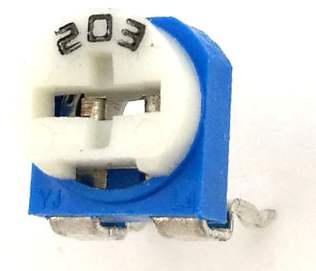
- Resistance: 203 20K Ohm,
- Resistor Tolerance: ±10% Max
- Max Voltage: 50V
- Rating Power: 0.1W
- Technology: Carbon Film
- Adjustment Type: Top Adjustment
-
- Resistance: 503 50K Ohm,
- Resistor Tolerance: ±10% Max
- Max Voltage: 50V
- Rating Power: 0.1W
- Technology: Carbon Film
- Adjustment Type: Top Adjustment
-
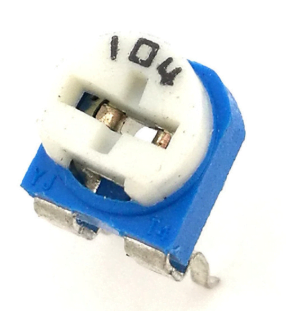
- Resistance: 100K Ohm,
- Resistor Tolerance: ±10% Max
- Max Voltage: 50V
- Rating Power: 0.1W
- Technology: Carbon Film
- Adjustment Type: Top Adjustment
-
- Bi-Polar NPN Transistor
- DC Current Gain (hFE) is 300 maximum
- Continuous Collector current (IC) is 200mA
- Base- Emitter Voltage (VBE) is 6V
- Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCE) is 40V
- Collector-Base Voltage (VCB) is 60V
- Available in To-92 Package
-
- Bi-Polar PNP Transistor
- DC Current Gain (hFE) is 300 maximum
- Continuous Collector current (IC) is 200mA
- Emitter Base Voltage (VBE) is 5V
- Base Current(IB) is 5mA maximum
- Collector Emitter Voltage (VCE) is 40V
- Collector Base Voltage (VCB) is 40V
- Available in To-92 Package
-
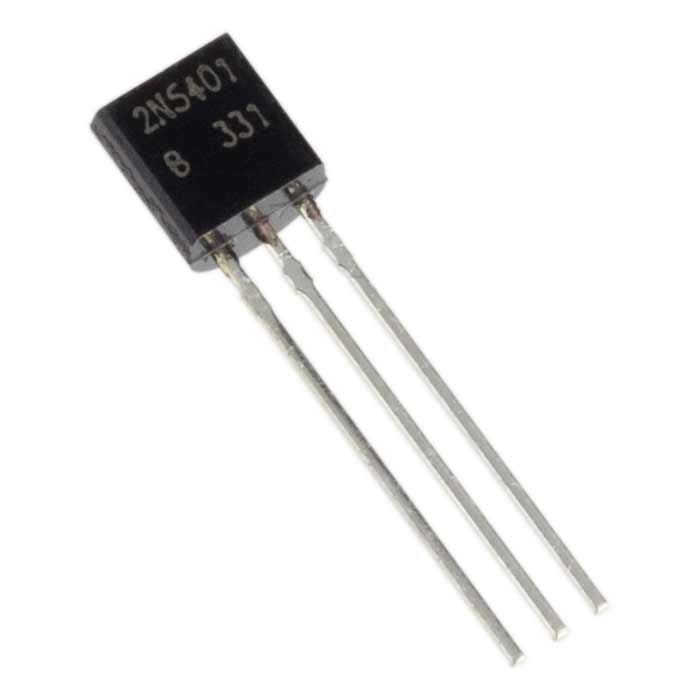
2N5401 Features and Electrical Characteristics
- Available in Pb Free package
- High collector breakdown voltage
- With DC Current Gain (hFE) up to 100
- Maximum voltage across collector and emitter: 150V
- Maximum current allowed trough collector: 600mA
- Maximum voltage across collector and base: 160 V
- Maximum voltage across base and emitter: 5V
- Operating temperature range: -55C to +150C
- Maximum power dissipation: 0.62 W
-
Features and Technical Specification
- Having a high value of current (max. 600 mA)
- Low voltage value (max. 40 V)
- It comes in different types of packages TO-92, TO-18
- These are Lead (Pb) free devices
- Collector to Emitter voltage (VCEO) is 40v (max.)
- Collector to Base voltage (VCBO) is 60v (max.)
- Emitter to Base voltage(VEBO) is 5v (normally)
- The maximum value of Collector current is 600mA
- Power dissipation at ambient temperature is about 400mW
- Having DC current gain (hfe) of 100 to 300 (max.)
- The temperature of operation and storage is -65 to +150 C
-
-
Overall height above PCB: 4.8mm
-
PCB hole required: 0.6mm
-
Pitch Width: 7.62mm (0.3in)
- Pin Pitch: 2.54mm (0.1in)
- Pins: 14 pins
-
-
14 Pin – DIP IC Socket/Base IC sockets are generally for preventing damage to IC’s from soldering and while testing multiple circuits. These are made from Black Thermoplastic and tin-plated alloy contacts. One end is notched to aid in identification. They can be mounted end to end to suit longer IC’s.
-
- Overall height above PCB: 4.8mm
- PCB hole required: 0.6mm
- Pitch Width: 7.62mm (0.3in)
- Pin Pitch: 2.54mm (0.1in)
- Pins: 16 pins
-
Specifications:
- Power (Watts) 1W
- Resistant 22K OHMS
- Tolerance +- 5%
- Resistor Type Carbon Film
- Lead Free
-
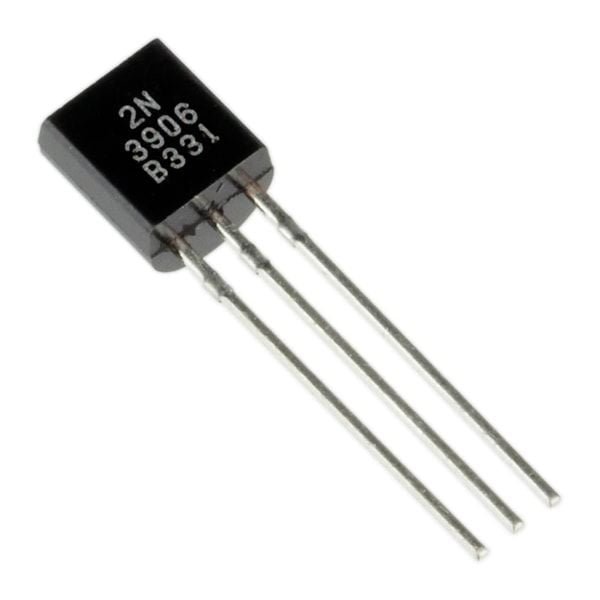
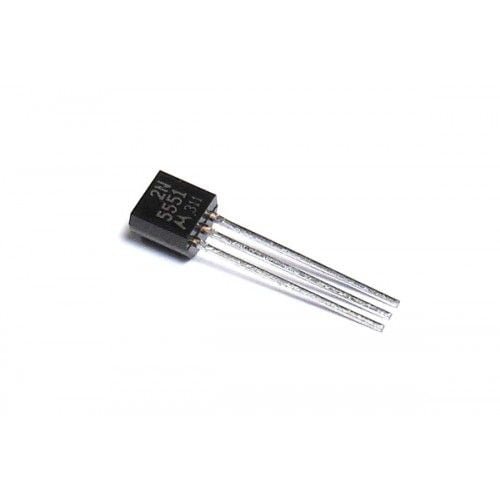
2N5551 is an NPN amplifier Transistor with an amplification factor (hfe) of 80 when the collector current is 10mA. The transistor is commonly used for amplification of audio or other low power signals.
-
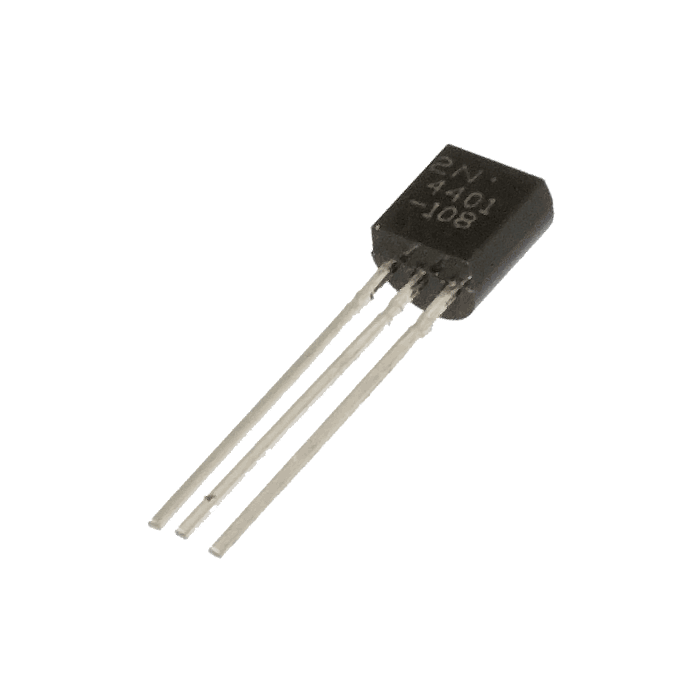
2N4401 is an NPN bipolar junction transistor that is mainly designed for general purpose, small signal, and switching applications.
-
The main use is for audio frequency amplifier applications. It can also be used for the switching purpose just like other PNP transistors. When use as an Audio frequency general purpose amplifier, can be operated in the active region. This transistor is further divided into four groups according to the DC current gain, O, Y, G, and L and has 140, 240, 400 and 700 hfe DC current gain respectively.
-
BC327 is a PNP bipolar junction transistor which is mainly designed for general purpose, small signal and switching applications.
-
- Xener Diode 9V
- Power 0.5W (1/2 watt)
- Good Quality
- Bread Board Mount
-
10V-1.5W Zener Diode, general purpose zener diode used in many circuits.
-
1N5822 40V 3A Schottky Rectifier Diode
Original price was: ₨20.00.₨15.00Current price is: ₨15.00. Quick View- Schottky Rectifier Diode
- Average forward current =3A
- Forward Surge Current =25A
- Forward Voltage Drop =600mV at 1A
- Peak reverse voltage =40V
- RMS Reverse Voltage =28V
- Forward Surge Current Ifsm Max =80A
- Diode Case Style =DO-27
-
Specification
- Origin: China
- Type: DIAC
Package Type: Through Hole - Package: DO-35
- Breakover Voltage: 28v to 36v
- Typical Breakover voltage: 32v
- Output voltage: 5v
- Breakover current: 50µA
- Leakage current: 10µA
- Peak current: 0.30A
- Rise time: 2µs
- Operating junction temperature: -40℃ to +125℃
- Storage temperature range: -40°c – +125°c
-
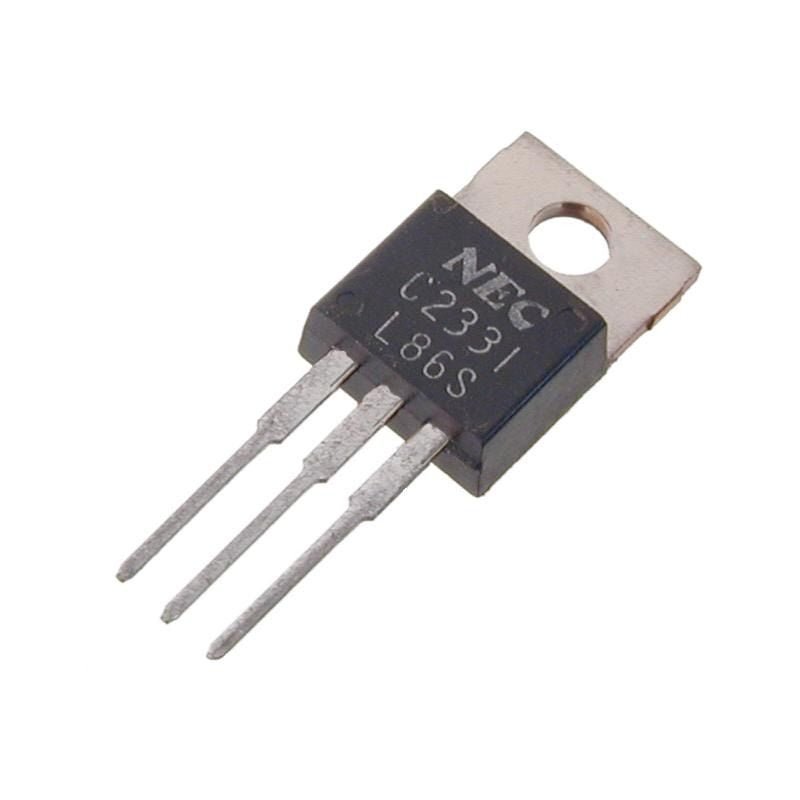
- Type Designator: 2SC2331
- Material of transistor: Si
- Polarity: NPN
- Maximum collector power dissipation (Pc), W: 1
- Maximum collector-base voltage |Ucb|, V: 80
- Maximum collector-emitter voltage |Uce|, V: 60
- Maximum emitter-base voltage |Ueb|, V: 8
- Maximum collector current |Ic max|, A: 0.7
- Transition frequency (ft), MHz: 30
- Collector capacitance (Cc), pF: 8
- Forward current transfer ratio (hFE), min: 40
- Noise Figure, dB: –
- Package of 2SC2331 transistor: TO92
-
- Case: R-6
- Case Material: Molded Plastic. UL Flammability Classification Rating 94V-0 Moisture Sensitivity: Level 1 per J-STD-020C
- Terminals: Finish Tin. Axial Leads, Solderable per MILSTD-202, Method 208
- Polarity: Color Band Indicates Cathode
- Approximate Weight: 2.1 grams
-
LM324 Operational Amplifier IC LM-324 consist of four independent high-gain frequency-compensated operational amplifiers that are designed specifically to operate from a single supply or split supply over a wide range of voltages. Wide Supply Ranges Single Supply: 3 V to 32 V (26 V for LM2902) Dual Supplies: 1.5 V to 16 V (13 V for LM2902) Low Supply-Current Drain.
-
The LM741 series are general-purpose operational amplifiers which feature improved performance over industry.The amplifiers offer many features : overload protection on the input and output, no latch-up when the common-mode range is exceeded, as well as freedom from oscillations. The LM741C is identical to the LM741 and LM741A except that the LM741C has their performance ensured over a 0C to +70C temperature range, instead of 55C to +125C.
-
- Low Voltage and Standard-Voltage Operation
- 2-wire Serial Interface
- Schmitt Trigger, Filtered Inputs for Noise Suppression
- Bi-directional Data Transfer Protocol
- 100kHz and 400kHz Compatibility
- Write Protect Pin for Hardware Data Protection
- 8-byte Page (1K, 2K), 16-byte Page (4K, 8K, 16K) Write Modes
- Partial Page Writes are Allowed
- Self-timed Write Cycle (10mS max)
-
A potentiometer knob is an accessory that is used as a control knob for a potentiometer.
-
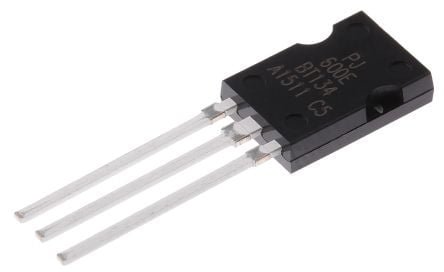
BT134 Triac – 600V – 4A (BT134-600E) Triac they are used in AC switching and control applications with current ratings from under 1A to 40A rms. Since TRIACs are bi-directional switching devices they are commonly used for switching AC applications. It has Maximum Terminal current: 4A, Max Terminal Voltage is 600 V, Gate trigger current: 25mA & On-state Gate voltage: 1.7V.
-
The SN74HC244N is an Octal Buffer and Line Driver IC, designed specifically to improve both the performance and density of 3-state memory address drivers, clock drivers and bus-oriented receivers and transmitters. This device organized as two 4-bit buffers/drivers with separate output-enable (OE)/inputs. When OE/ is low, the device passes non-inverted data from the A inputs to the Y outputs. When OE/ is high, the outputs are in the high-impedance state.
-
The 4072 is a member of the 4000 Series CMOS range, and contains two independent OR gates, each with four inputs.
-
The CD4040 is a 12-stage ripple carry binary counter. The counters are advanced one count on the negative transition of each clock pulse. The counters are reset to the zero state by a logical 1 at the reset input independent of the clock.
-
A heat-sink is designed to remove heat from a transistor and dissipate it into the surrounding air as efficiently as possible. Heat-sinks take many different forms, such as finned aluminium or copper sheets or blocks, often painted or anodised matt black to help dissipate heat more quickly. Good physical contact between the transistor and heat-sink is essential, and a heat transmitting grease (heat-sink compound) is smeared on the contact area before clamping the transistor to the heat-sink.
-
DF005S Diode Bridge Rectifier 1.5A SOP-4 SMD
Original price was: ₨27.00.₨22.00Current price is: ₨22.00. Quick ViewBridge Rectifiers for PCB Surface Mount.
-
The voltage regulator IC maintains the output voltage at a constant value. 7805 provides +5V regulated power supply. Input voltage range 7V- 35V Current rating Ic = 1A Output voltage range VMax=5.2V ,VMin=4.8V.
-
BC134 is a NPN type transistor. Its Maximum Collector-Base Voltage |Vcb|: 45 V & Maximum Collector Current |Ic max|: 0.2 A.
-
BC109 is a bipolar NPN type transistor. It has Collector-Emitter Volt (Vceo): 20V & Collector Current (Ic): 0.2A.
-
- 15V Positive Voltage Regulator
- Minimum Input Voltage is 17V
- Maximum Input Voltage is 35V
- Output Current: 1.5 A
- Internal Thermal Overload and Short circuit current limiting protection is available.
- Junction Temperature maximum of 125 degree Celsius
- Available in TO-220, TO-3 and KTE package
-
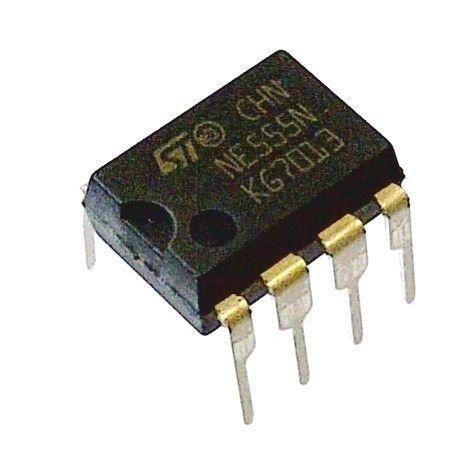
- It works from a wide range of power supplies ranging from +5V to +18V.
- Sourcing or sinking load current is 200mA.
- The external components must be selected correctly, so that the timing intervals can be completed in several minutes along with the frequencies beyond several hundred kHz.
- The o/p of a 555 timer IC can drive TTL due to its high current o/p.
- It takes a temperature stability of 50 ppm/oC change in temperature (ppm means parts per million)
- The timers duty cycle is adjustable.
- The max power dissipation per package is 600 milliwatts & its reset and trigger i/ps has logic compatibility.
-
Texas Instruments SN7414 Series Inverters are available at ElectroNation.
-
- Carries Low input bias current = 50 pA
- Available with Low input noise current = 0.01 pA/Hz
- Comes with Fast settling time to 0.01% = 2us
- Contains internally trimmed offset voltage = 15 mV
- Carries Low input noise voltage = 16nV/Hz
- Exhibits Low supply current = 3.6 mA
-
- Type – NPN
- Collector-Emitter Voltage: 25 V
- Collector-Base Voltage: 30 V
- Emitter-Base Voltage: 7 V
- Collector Current: 0.05 A
- Collector Dissipation – 0.4 W
- DC Current Gain (hfe) – 130 to 520
- Transition Frequency – 220 MHz
- Noise Figure – 6 dB
- Operating and Storage Junction Temperature Range -55 to +150 °C
- Package – TO-92
-
- 2sc925 well known as C945 NPN transistor.
- Max Voltage Collector Emmiter=50 V.
- Max Collector current=150 mA.
- Collector power dissipation: 400 mW.
- Japanese High-frequency amplifier NPN Transistor.
- Current Gain (hFE) is 70 to 700 (high linearity).
- Continuous Collector current (IC) is 150mA.
- Collector-Emitter voltage (VCEO) is 50 V.
- Collector-Base voltage (VCB0) is 60V.
- Emitter Base Voltage (VBE0) is 5V.
- Transition Frequency is 150MHz.
-
LM386 LM-386 Audio Amplifier Chip
Original price was: ₨35.00.₨29.00Current price is: ₨29.00. Quick ViewLM386 is a widely used audio amplifier IC manufactured in 8 pin dip, VSSOP, SOIC and other packages. The IC is basically designed for low voltage commercial applications, apart from commercial applications it is also a famous IC among electronic hobbyists and experimenters. The internal gain of the IC is set to 20 but it can be adjusted by connecting a resistor and a capacitor in series between the pin number 1 and 8, by this procedure the user can adjust the gain between 20 to 200. Due to the small size, low quiescent current and low voltage requirements this IC is ideal to use in wide variety of portable battery operated applications and devices.
-
LM393 Dual COMPARATOR Low Offset Voltage IC
Original price was: ₨45.00.₨29.00Current price is: ₨29.00. Quick View- Voltage Comparator circuits
- Can drive Relay, Lamp, Motor Etc
- Zero Crossing detector
- Peak voltage Detector
- High Voltage protection/Warning
- Oscillator circuits