2N5401 Transistor Overview
2N5401 is specifically designed to be used in high-voltage applications where the load consumes very little power (i.e. Current drawn by the load is low). These types of circuits can be seen in telephone systems. It can also be used when you want a simple switching device for high-voltage loads. Also, the component is cheap and easy to work with.
How to Use 2N5401 Transistor
2N5401 can be used like any general-purpose PNP transistor but for the sake of understanding the device working let us consider a simple application circuit as shown below.
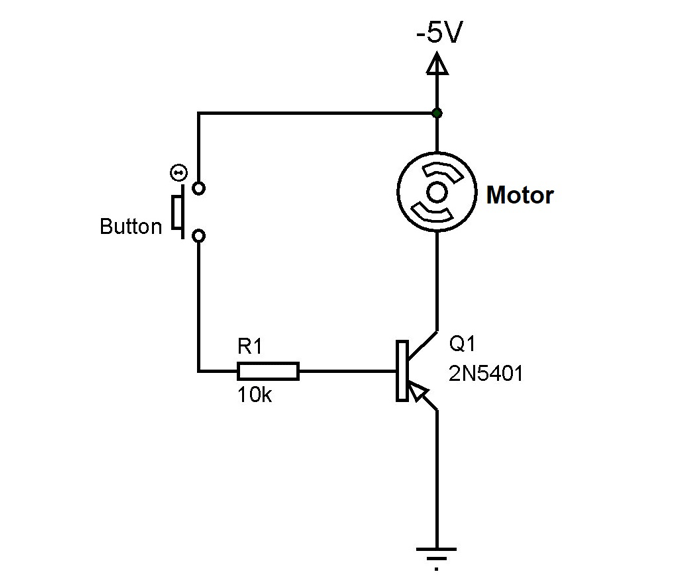
In the above circuit, we are using 2N5401 as a simple switching device and the switching load is a small DC motor. The button here is for providing the trigger to the transistor and the 10K resistor is for limiting the current to the base and to avoid breaching the maximum voltage allowed at the base. Also as pointed out in the comment section below, considering the low gain of this transistor, it might be a better idea to use a low-value resistor like 100R for R1 to allow more base current. The circuit is powered from a negative voltage source of -5V DC as shown in the diagram.
Before going to work let us revise the typical characteristics of a PNP transistor:
- The device does not conduct when the current does not flow out of the base of the transistor or the device conducts only when the base current that flows out of the device reaches a threshold.
- The current flow through the collector is determined by the base current to a certain point. So with a higher gate current, we have lower conduction resistance and a higher collector current.
- The PNP transistor conducts only when a threshold current flows out of the base, so the instant the base current reaches zero the device stops conducting.
Consider the button is not pressed: When the button is not pressed there will be no base current and with no base current the transistor will not conduct based on the characteristics of the PNP transistor. When the transistor does not conduct the entire voltage appears across it and the motor will be OFF.
Consider the button is pressed: When the button is pressed, the base of 2N5401 will be connected to the negative power supply and so there will be a path for the current flow. When the base current flows out from the device it will start conducting as stated in characteristics. In the presence of this collector current flow, a voltage appears across the motor connected in series with the collector pin. In the presence of the voltage the motor will start rotating and it will stay like that until the button is released. The moment the button is released the base current will reach zero, thereby turning OFF the transistor and the motor.
In this way, we can turn the motor ON and OFF by using a simple button as a trigger and 2N5401 as a switching device. In high-speed switching, the trigger is provided by a microcontroller instead of a button.
Applications
- General purpose switching and amplification
- Telephony applications
- High voltage application








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.